User Experience (UX) principles play a vital role in shaping how people interact with products, services, and systems in everyday situations. Key UX Principles in Everyday Situations. Here are some key UX principles and how they apply to various scenarios:
- Clarity and Simplicity: Make interfaces and interactions simple and clear. Whether it’s a website, app, or physical product, avoid unnecessary complexity. For example, a microwave should have intuitive buttons with clear labels for different functions.
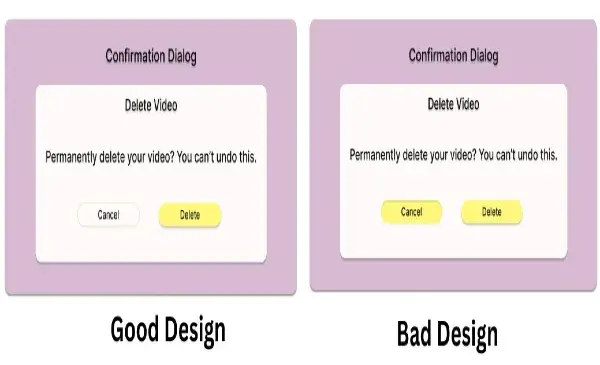
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent design and behavior throughout the experience. Users should be able to predict how things work based on previous interactions. In a messaging app, consistent placement of send buttons and similar icons creates a smoother experience.
- Visibility: Ensure important elements are easily visible. In a grocery store, placing essential items at eye level makes it convenient for shoppers to find what they need quickly.
- Feedback: Provide feedback to users for their actions. A progress bar when uploading files or a confirmation message after submitting a form reassures users that their actions were successful.
- Efficiency and Speed: Minimize the time it takes for users to achieve their goals. Search engines prioritize showing relevant results quickly, so users can find information efficiently.
- Flexibility and Control: Allow users to customize their experience. Video streaming platforms let users control playback speed, subtitles, and video quality, catering to individual preferences.
- Error Prevention and Recovery: Design interfaces to prevent errors and offer clear paths for recovery. Autocomplete in search bars helps users find what they’re looking for, reducing the chance of mistyped queries.
- Accessibility: Ensure your design is usable by people with disabilities. Websites should have text alternatives for images, and apps should be navigable using screen readers.
- Aesthetics and Consistency: Design should be aesthetically pleasing, but also consistent with the brand’s identity. A well-designed cafe not only offers great coffee but also provides a visually pleasing ambiance.
- User-Centered Design: Prioritize user needs and behaviors in your design decisions. A fitness app should align with users’ health goals and make it easy to track progress.
- Minimize Cognitive Load: Avoid overwhelming customers with an excessive amount of data at once. A public transportation app should present the most relevant options first, simplifying the decision-making process.
- Storytelling: Create a narrative or flow that guides users through their journey. A museum exhibit should lead visitors through a logical sequence, making it easy to understand the context and significance of each display.
- Contextual Awareness: Design experiences that adapt to the user’s context. A smart thermostat learns users’ schedules and adjusts the temperature accordingly.
- Emotional Design: Evoke positive emotions through design. A meditation app might use calming colors and soothing sounds to create a relaxing atmosphere.
- User Testing and Iteration: Continuously gather user feedback and make improvements. This applies to everything from website navigation to the layout of a physical store.
- Cross-Platform Consistency: Maintain consistency throughout exceptional structures and devices. A banking app should offer a similar experience on both its website and mobile app.