Empathy mapping UX 2024
Empathy mapping in UX design is a technique used to gain a deeper understanding of users’ emotions, motivations, and behaviors by putting oneself in their shoes. It involves creating a visual representation of the user’s experience and mindset.
Focusing on what they see, hear, think, feel, say, and do. Here’s how empathy mapping works in UX:
Define the User Persona: Start by identifying the user persona or segment you want to empathize with. This persona represents a fictional but realistic representation of your target user, including their demographics, goals, needs, and pain points.
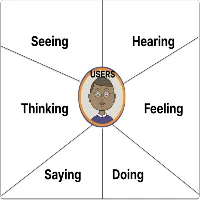
Create the Empathy Map: Draw a large canvas or use a digital tool to create a grid with six quadrants representing the following aspects:
Seeing: What does the user see in their environment? What catches their attention visually?
Hearing: What does the user hear in their surroundings? What conversations or sounds are present?
Thinking: What thoughts go through the user’s mind? What worries, concerns, or aspirations do they have?
Feeling: What emotions does the user experience? How do they feel about their current situation or task?
Saying: What words or phrases does the user use to express themselves? What do they communicate verbally or in writing?
Doing: What actions does the user take? How do they behave or interact with their environment?
Collect Insights: Gather insights about the user’s experience by conducting research, interviews, observations, or usability testing. Use qualitative data such as quotes, observations, and anecdotes to inform each quadrant of the empathy map.
Fill in the Quadrants:
Populate each quadrant of the empathy map with relevant observations, insights, and quotes that capture the user’s experience. Use sticky notes, sketches, or symbols to represent each observation.
Identify Patterns and Opportunities:
Analyze the completed empathy map to identify patterns, themes, and opportunities for improving the user experience. Look for common pain points, unmet needs, and emotional triggers that can inform design decisions.
Brainstorm Solutions:
Use the insights from the empathy map to brainstorm potential design solutions that address the user’s needs and emotions. Consider how you can design experiences that resonate with the user’s mindset and enhance their overall satisfaction.
Iterate and Refine: Continuously iterate and refine the empathy map based on new insights, feedback, and testing. Update the map as you learn more about the user’s experience and refine your understanding of their needs and motivations.
Collaborative Approach: Empathy mapping is most effective when done collaboratively with cross-functional teams, including designers, researchers, product managers, and stakeholders. Collaborative sessions allow for diverse perspectives and insights, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the user’s experience.
Include Diverse Perspectives: When creating empathy maps, consider the diversity of your target audience. Include insights from users with different backgrounds, experiences, and needs to ensure that the map reflects a broad range of perspectives.
Focus on Empathy, Not Assumptions: Empathy mapping is about understanding the user’s experience from their perspective, not making assumptions based on your own biases or preferences. Approach the process with an open mind and a genuine desire to empathize with the user’s emotions and motivations.
Use Visuals Effectively: Visual elements such as icons, symbols, colors, and images can enhance the clarity and impact of empathy maps. Use visuals to represent key insights and emotions, making the map more engaging and memorable for stakeholders.
Iterate and Iterate: Empathy mapping is an iterative process that evolves as you gather more insights and feedback. Continuously revisit and refine the empathy map based on new research findings, user feedback, and changes in user behavior.
Consider Context and Environment: Pay attention to the context and environment in which users interact with your product or service. Consider how factors such as location, time of day, device used, and social surroundings influence the user’s experience and emotions.
Test and Validate: Validate the insights from the empathy map through user testing and validation. Use usability testing, interviews, surveys, and other research methods to verify that your assumptions about the user’s experience are accurate and representative.
Integrate with User Journey Mapping: Integrate empathy mapping with user journey mapping to create a more holistic understanding of the user’s experience. Use empathy maps to inform specific touchpoints and stages of the user journey, identifying opportunities for improvement and optimization.
Empathy as a Mindset: Beyond empathy mapping exercises, cultivate empathy as a mindset within your design team and organization. Encourage team members to regularly engage with users, listen to their feedback, and empathize with their needs and perspectives throughout the design process.
Empathy mapping is a valuable tool in UX design for fostering empathy, uncovering user insights, and informing design decisions that prioritize the user’s needs and emotions. By creating empathy maps, designers can develop more empathetic and user-centered solutions that resonate with their target audience. Empathy mapping UX 2024