Video production involves several phases, each crucial for creating a high-quality and compelling video. These phases are often sequential and may overlap in some cases. Here are the main phases of video production:
Development – It is the 1st step of Video Production. It is also an important step for Video production.
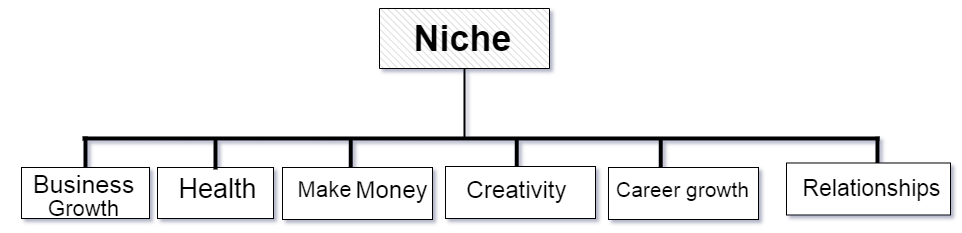
In this phase, the organization discusses what sort of video they want. They work on the layout. They work on ideas. The first step in video production is to discuss with the client what they want and how they achieve with their video and determine how to build upon their initial thinking.
They focus on the types of audiences they want or project needs—the initial plan on how to execute the idea. Knowing your target audience knows how you shape your final video.
It includes Draft Script writing, From the Draft script you get budget ideas. In the script also there are different types of length of videos.
The length of the script depends on any clips or movies. It also includes the moment a Producer thinks of a project. It is a time for writer to do their wonderful work.
Pre-Production:
- Concept Development: This is the initial stage where the idea for the video is conceived. It involves brainstorming, research, and defining the purpose and message of the video.
- Scriptwriting: Once the concept is established, a script is written. The script outlines the narrative, dialogue, and visual elements of the video.
- Storyboarding: Visualizing the script through a series of illustrations or images helps in planning the shots and sequences.
- Budgeting and Scheduling: Planning the budget and schedule for the entire production process, including equipment, locations, personnel, and post-production.
Production:
- Filming/Recording: This phase involves capturing the planned footage according to the script and storyboard. It includes setting up cameras, lighting, and audio equipment.
- Directing: The director is responsible for guiding the actors and crew to ensure the vision outlined in the script is effectively captured.
- Capturing Additional Footage (B-Roll): Additional shots, known as B-Roll, may be captured to enhance the video during the editing phase.
- Managing Logistics: Coordination of various elements, such as scheduling, locations, and equipment, to ensure a smooth production process.
Post-Production:
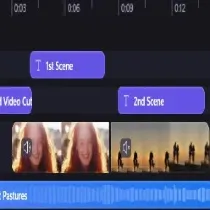
- Editing: The raw footage is assembled and edited to create the final sequence. This includes cutting unnecessary scenes, adding transitions, and incorporating visual effects if needed.
- Sound Design: Enhancing or adding sound elements, including music, sound effects, and voiceovers, to complement the visuals.
- Color Grading: Adjusting the color and tone of the footage to achieve a consistent and desired look.
- Visual Effects (VFX): If required, add computer-generated effects to enhance the video.
- Titling and Graphics: Adding titles, credits, and any necessary graphics to convey information.
- Review and Feedback: Iterative reviews are conducted, and feedback is incorporated to refine the video.
Distribution and Marketing:
- Distribution Strategy: Planning how and where the video will be released, whether on a specific platform, website or through other channels.
- Marketing: Promoting the video to the target audience through various means, including social media, email campaigns, and advertising.
Evaluation:
- Analyzing Performance: After the video is released, metrics such as views, engagement, and feedback are analyzed to evaluate its success and gather insights for future projects.
Each of these phases requires careful planning, coordination, and attention to detail to ensure the final video meets its intended goals and resonates with the target audience. The collaborative effort of a skilled team, including producers, directors, cinematographers, editors, and more, is crucial for a successful video production process.