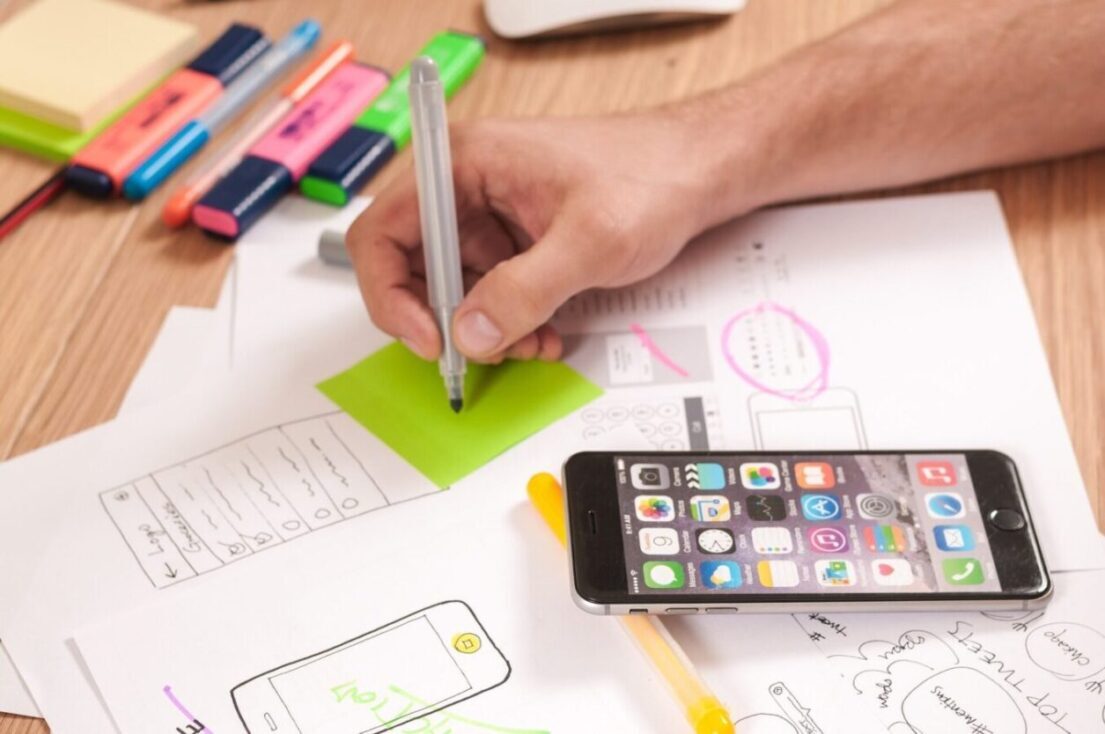
Technology user personas in UX design refer to fictional representations of specific user segments within the context of technology products, services, or digital experiences. These personas are created based on research and data about real users who interact with technology. Such as websites, mobile apps, software applications, or digital platforms.
Here are some key components and considerations for technology user personas in UX design:
Multi-Platform Usage:
User personas may encompass users who interact with technology across multiple platforms and devices. This includes considerations for seamless experiences across desktop, mobile, tablet, and other digital platforms. As well as transitions between different devices.
Technological Proficiency:
User personas should outline the level of technological proficiency and familiarity with digital tools and platforms. This includes factors such as experience with computers, smartphones, tablets, internet usage, and familiarity with specific software or applications.
Device Preferences:
User personas may include information about the devices and platforms preferred by the target users. Such as desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, or tablets. Understanding device preferences helps designers optimize the user experience for different screen sizes and form factors.
Behaviors and Usage Patterns:
User personas describe the typical behaviors, usage patterns, and interactions of users with technology products or digital experiences. This includes how often users engage with technology, what tasks they perform, and how they navigate through digital interfaces.
Goals and Objectives:
User personas outline the specific goals, objectives, and motivations that drive users to interact with technology products or digital platforms. This includes both functional goals (e.g., completing a task, finding information) and emotional goals (e.g., feeling entertained, connected, or empowered).
Challenges and Pain Points:
User personas identify the challenges, pain points, frustrations, and obstacles that users may encounter while using technology products or digital experiences. Understanding these pain points helps designers address user needs and improve the user experience.
User Environment:
User personas should consider the context in which users interact with technology, such as their physical environment, time constraints, distractions, and any external factors that may influence their behavior or preferences.
Accessibility and Inclusivity:
User personas should account for accessibility considerations, ensuring that technology products and digital experiences are usable and accessible to users with disabilities or diverse needs. Designers should consider factors such as visual impairments, motor disabilities, and cognitive limitations when creating user personas.
Personalization and Customization:
User personas enable designers to personalize and customize the user experience to meet the specific needs and preferences of different user segments. This may involve offering personalized recommendations, adaptive interfaces, or customizable settings based on user preferences.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations:
User personas should take into account ethical and privacy considerations related to the collection and use of user data in technology products and digital experiences. Designers should respect user privacy rights and ensure transparency, consent, and data security in their designs. Technology User Persona in UX 2024
Overall, technology user personas play a crucial role in UX design by providing designers with insights into the needs, behaviors, preferences, and motivations of target users within the context of technology products and digital experiences. By creating user personas, designers can develop user-centered design solutions that effectively meet the needs and expectations of their target audience. Technology User Persona in UX 2024